Outbound Traffic Control
An additional control layer is to verify outgoing traffic (Outbound VPC traffic), to ensure that your instances are only communicating where it is desirable and expected, like connecting to the manufacturer of an operating system or application for updates, and not to malicious URLs/IP addresses, or establishing tunnels for remote access.
There are multiple ways to control outgoing traffic on AWS.
Route 53 Resolver DNS Firewall
With Route 53 Resolver DNS Firewall you can filter and regulate outbound DNS traffic for your virtual private cloud (VPC). It’s recommended to deny access to all domains except for the ones that you explicitly trust. It’s easy to implement and simple to deploy through AWS Firewall Manager in a multi-account environment.
Note: This type of firewall will not prevent an outgoing connection to a IP address, but most malware outgoing connections are to URLs, and many time the infection can be prevented by disallowing the fetching of the malware in the first place.
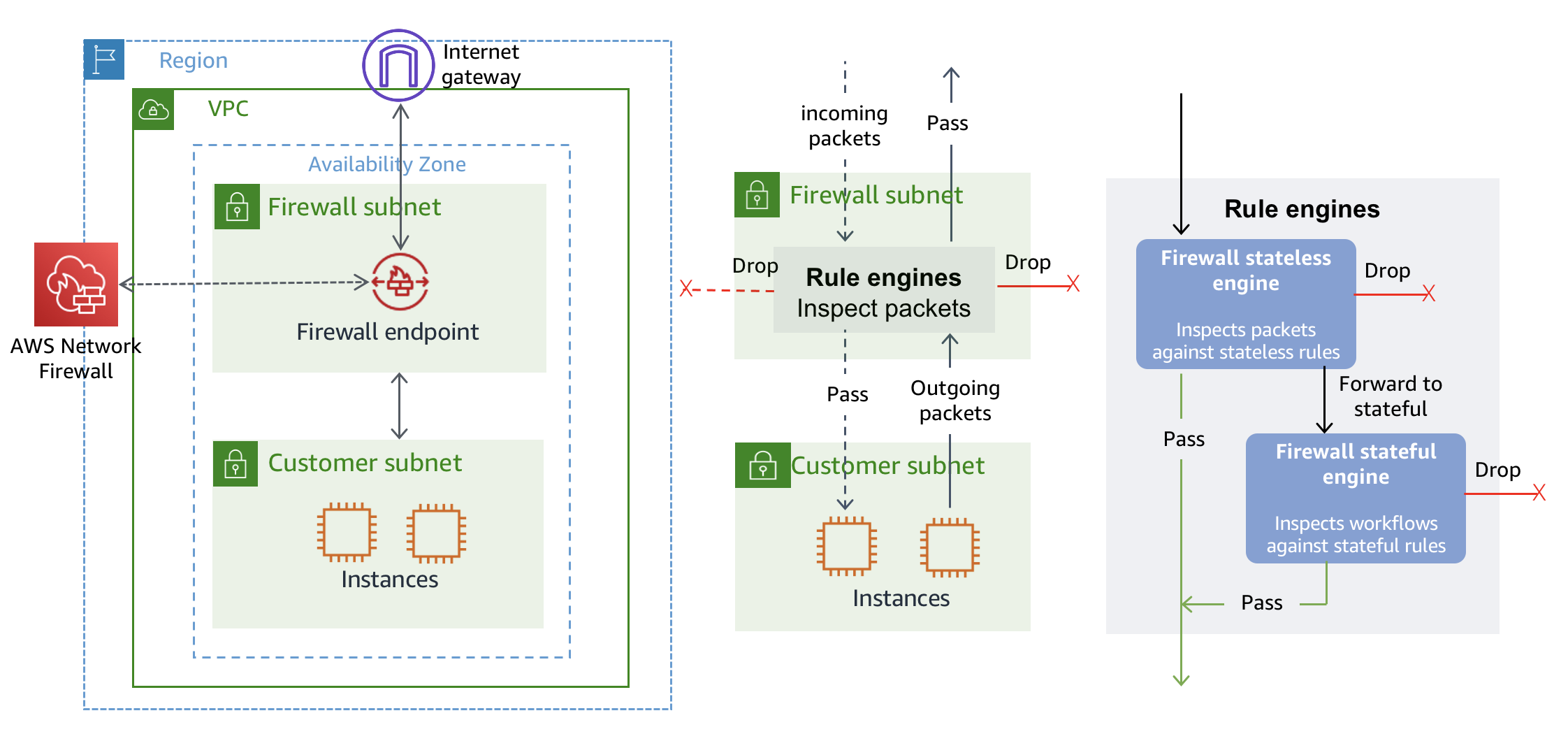
AWS Network Firewall
AWS Network Firewall is able to analyze incoming and outgoing traffic in layer 3 to layer 7. More information in the following Blogpost
You can also use any of the Next-Gen Firewall / UTM solutions available in the AWS Marketplace to filter outgoing traffic.
PrivateLink
Use AWS PrivateLink To establish private communications with the VPCs of your business associates when possible, so that such traffic does not go over the internet.
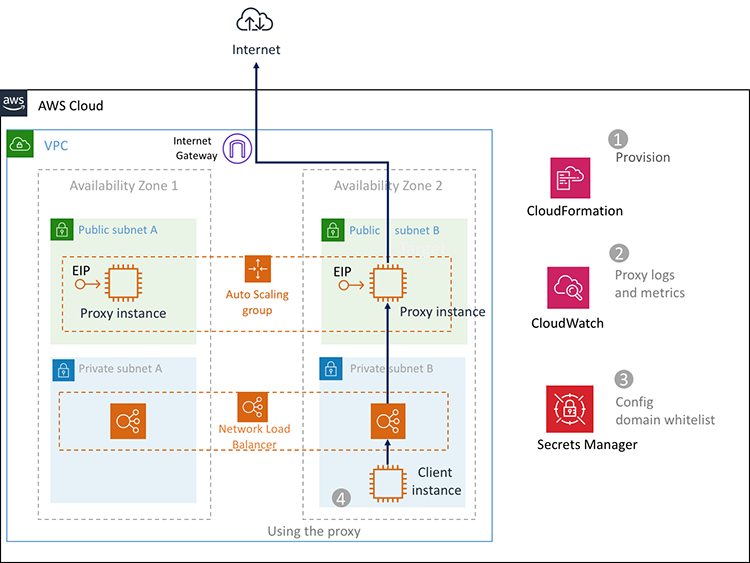
Deploying a proxy for outgoing access control
The following blogpost explains how to deploy a proxy (Squid) for outgoing traffic filtering and provides a CloudFormation template to facilitate its deployment:
How to set up an outbound VPC proxy with domain whitelisting and content filtering
East-west inspection
Review the Deployment models to learn more on how to deploy your AWS Networ firewall for VPC to VPC Inspection or from on-prem to VPC inspection
Ingress filtering
Ingress filtering with a network firewall makes sense if you’re sharing services other than web, as AWS Network Firewall or 3rd party firewalls provide IPS capabilities that will prevent the exploitation of vulnerabilities in these services, but if you’re only sharing web applications, a WAF will provide you Layer 7 inspection, reducing the use cases where including a network firewall in your architecture makes sense
SIEM Integration
If there is a SIEM consider sending the logs of the service (or virtual appliance) filtering trafic (such as Next-gen firewalls or proxys) for the detection of Shadow IT, and the configuration of other alerts.
Prices
AWS Route53 Resolver DNS Firewall
https://aws.amazon.com/route53/pricing/#Route_53_Resolver_DNS_Firewall
AWS Network Firewall
https://aws.amazon.com/network-firewall/pricing/