Limit Network Access using Security Groups
Always grant the minimum required permissions in Security Groups (least privilege).
Check that granted permissions are as intended, as developers often create open security groups for testing and forget to close them before moving them to production.
Closing risky open ports in Security Groups is the first to do, but all security groups, especially for critical applications should be reviewed, in particular open ports other than web, and internal web applications allowing access from everywhere.
You can use the AWS Config restricted-common-ports rule by indicating different ports as parameters to detect open ports.
Use references in security groups
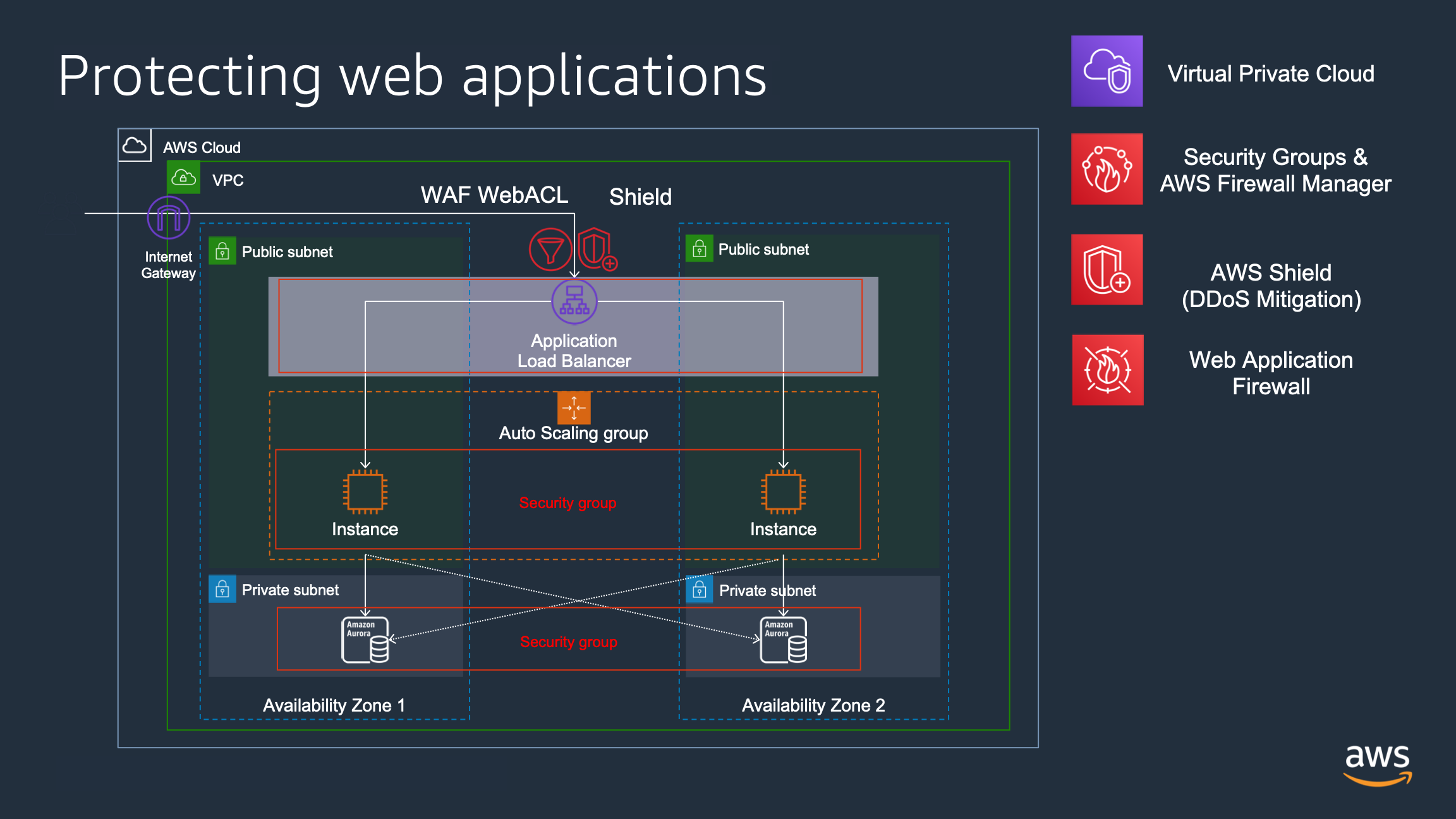
Another recommendation is the use of references in security groups, for example, in a web application:
- An Application Load Balancer with Security Group “sg-alb” allows inbound connections to port 80/443
- An Autoscaling group with web servers in multiple availability zones using Security Group “sg-webservers” allowing traffic to port 80/433 only from resources using Security Group “sg-alb” (only from load balancer).
- A database service, such as Amazon Aurora or Amazon RDS configured with a Security Group “sg-db” allowing traffic to port 3306 only from instances with Security Group “sg-webservers”.
Thus in this way, web instances only serve traffic that comes from the ALB, where you can configure AWS WAF , ensuring that all inbound traffic to web instances has been inspected. The database service only serves requests from web servers, and if a new instance is added by autoscaling, it will be added to the security group and will be able to access the database.
Leveraging AWS Firewall manager to detect overpermissive Security Groups
You can leverage AWS Firewall Manager to audit Security Groups and enforce rules centrally in multiple accounts, identifying overly permissive SGs, idetifying access to high risk applications, and cleaning up unused and redundant SGs. Depending on the size of the organization and how your resources are created (manually vs. using Infrastructure as code) the use of this service will be optional or strongly recommended. Learn more in the following presentation: User AWS Firewall Manager to audit overpermissive security groups
Risk Mitigation
- Misconfigured security groups allow adversaries to attempt to exploit vulnerabilities on the services that offer network visibility.
- Developers often allow broad access in Security Groups arguing “I’ll restrict that later” and often they don’t.
Guidance for assessments
- Who in your organization defines the security groups ? are they trained to only allow minimum permissions? or untrained developers create the security groups without control/supervision?
- [If varies on the organization] Are critical applications configured to allow only the minumum ports?
- Are internal applications allowing traffic from anywhere ?
- Are you leveraging AWS Firewall Manager or a similar solution to identify and audit overpermissive security groups? What rules have you configured?
Pricing
Security groups have no additional cost.
If you choose to use AWS Firewall Manager : https://aws.amazon.com/firewall-manager/pricing